Acrel develops and produces various types of power sensors. Based on different application scenarios, different measurement ranges, and different installation methods, we design AKH-0.66 series measuring current transformers, protective current transformers, and residual current transformers. transformers, open-type current transformers, metering current transformers to BA series current sensors, BD series power transmitters, BM series analog signal isolators and other power sensors. It is easy to install, small in size, high in accuracy, beautiful in appearance, large in capacity, convenient in wiring, strong in overload capacity and strong in anti-interference ability.
By carefully considering these factors and specifications, you can select the most appropriate power sensor for your application, ensuring accurate and reliable power measurements.
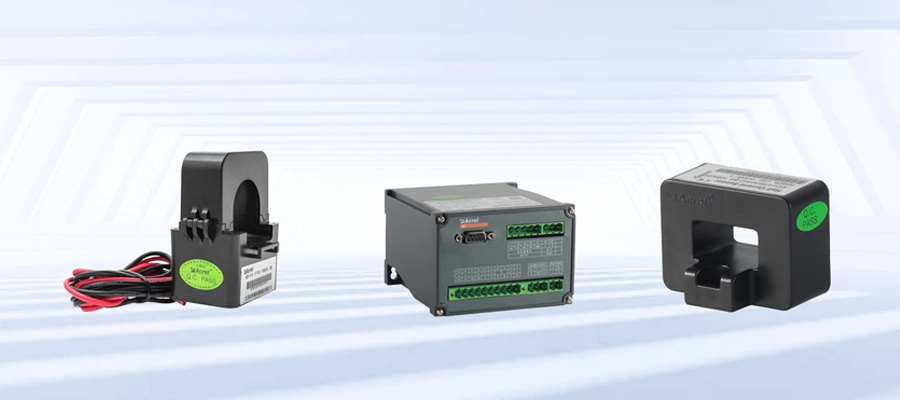

A power sensor works by measuring the electrical power flowing through a circuit or device. It typically measures parameters such as voltage, current, and phase angle to calculate power consumption. The sensor may use various technologies such as Hall effect sensors, current transformers, or Rogowski coils to detect and measure these parameters accurately. Once the measurements are obtained, the sensor processes the data to calculate the instantaneous or average power consumed by the load. This information can be used for monitoring energy usage, power quality analysis, or implementing control strategies for efficient power management.