
Energy meters, commonly known as watt-hour meters, operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction. They measure the amount of electrical energy consumed by a load over a period of time. Inside the meter, there is typically a rotating disc or a solid-state sensor. When electricity flows through the meter, it creates a magnetic field around the conductors. This magnetic field interacts with the disc or sensor, causing it to rotate. The rotation of the disc or movement of the sensor is proportional to the amount of electrical energy passing through the meter.
In traditional electromechanical energy meters, the rotating disc is attached to a shaft connected to a series of gears. As the disc rotates, it turns a series of gears that drive the numerical dials on the meter's display. Each revolution of the disc corresponds to a specific amount of energy consumption, allowing the meter to accurately measure and record the energy usage.
In solid-state electronic energy meters, the movement of the sensor generates electrical pulses. These pulses are then counted and processed by electronic circuitry within the meter. The processed data is used to calculate the energy consumption, which is then displayed on a digital readout.
Overall, energy meters measure electricity consumption by converting the mechanical or electronic movement generated by the flow of electricity into readable data that indicates the amount of energy used.
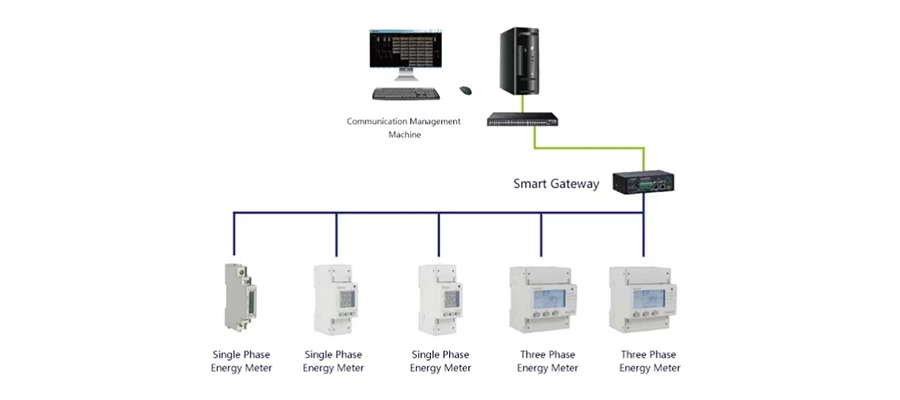
Electricity meters are typically connected in series with the main power line entering a building or facility. The incoming power line is routed through the meter, where it is measured for consumption. The meter may be installed indoors or outdoors, depending on local regulations and preferences. After passing through the meter, the power line continues to the main distribution panel, where it is distributed to various circuits and loads within the building. The meter may also be equipped with a disconnect switch to enable the utility provider or authorized personnel to disconnect power in case of maintenance or emergencies.